The Long and Short Strangle
The Long Strangle and Short Strangle strategies are options techniques used for trading based on expectations of significant price movement or stability.
Long Strangle
This strategy involves buying a call and a put option at different out-of-the-money strike prices, anticipating high volatility.
- Profit Potential: Unlimited if the asset moves sharply in either direction.
- Maximum Loss: Limited to the premiums paid if the asset remains stable.
Short Strangle
This strategy involves selling a call and a put option at different out-of-the-money strike prices, collecting premiums with the expectation of low volatility.
- Profit Potential: Limited to the premiums collected.
- Risk: Unlimited if the asset moves significantly outside the strike prices.
How It Works
-
Long Strangle Setup:
- Buy an out-of-the-money call and an out-of-the-money put.
- Profit is achieved if the asset moves significantly in either direction.
-
Short Strangle Setup:
- Sell an out-of-the-money call and an out-of-the-money put.
- Profit is achieved if the asset remains range-bound.
Long Strangle on AlgoTest
Go to AlgoTest’s Strategy Builder by clicking on this link. You will get an interface as shown in the image below.
Go to Settings and select Spot to run the strategy.
From the Option Chain, we just have to:
- Buy 1 lot of OTM call options
- Buy 1 lot of OTM put options
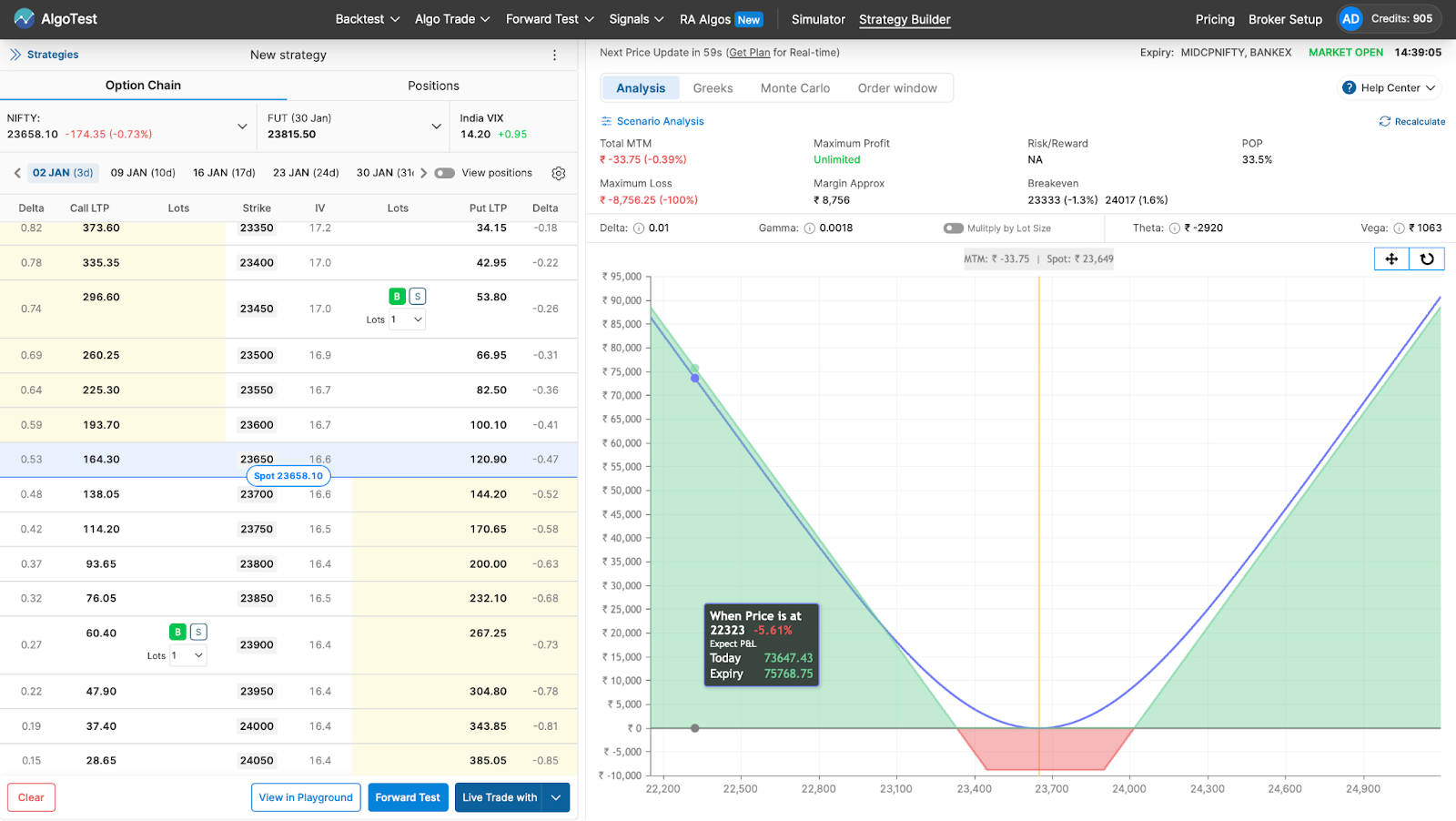
Click the Buy/Sell button as shown in the image below.
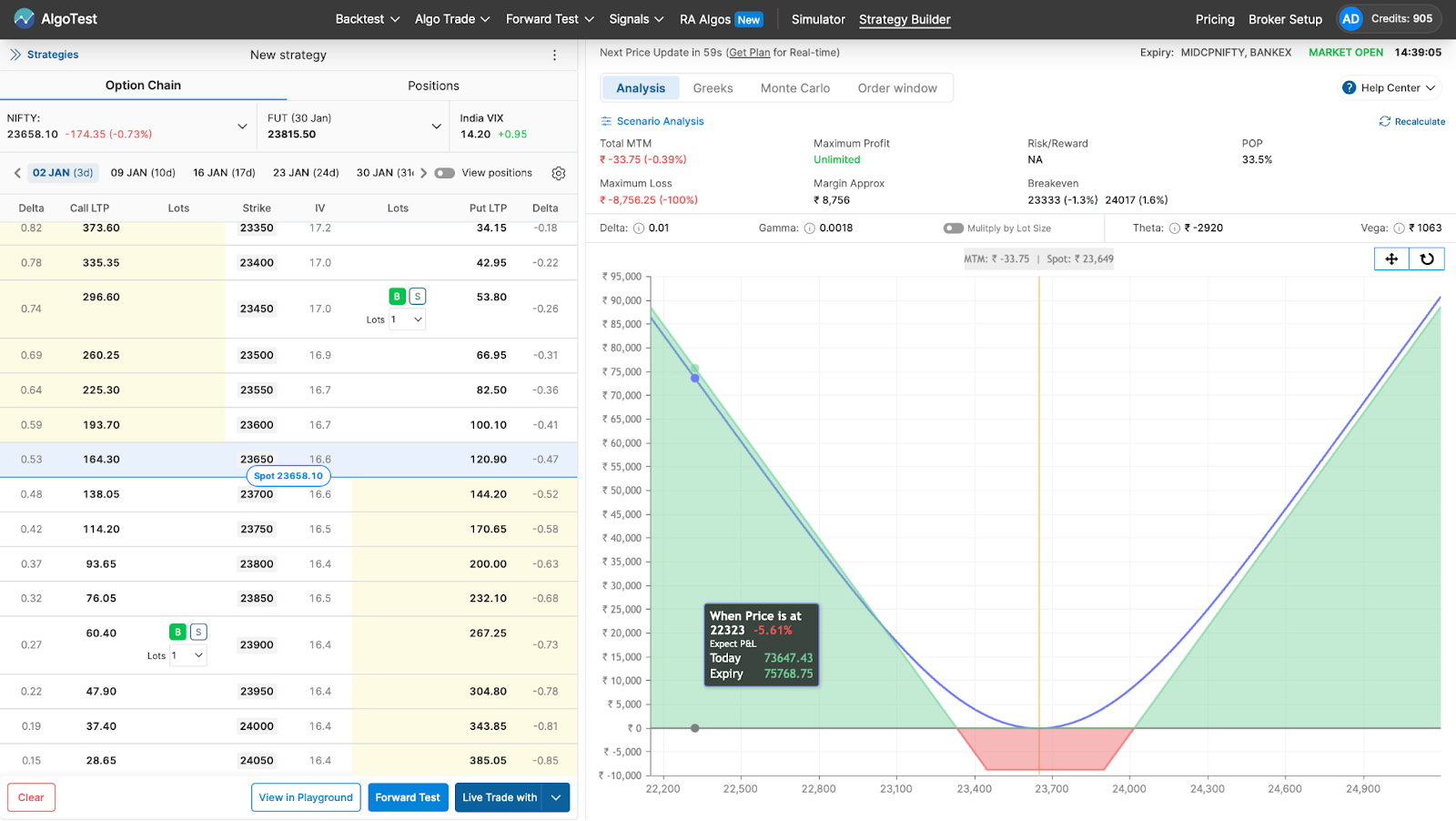
After that, you can deploy it on your broker in one click by clicking the Live Trade With button as shown in the image below. Alternatively, you can forward test (paper trade) it on AlgoTest if you don’t want to deploy it with real money.
Short Strangle on AlgoTest
Go to AlgoTest’s Strategy Builder by clicking on this link. You will get an interface as shown in the image below.
Go to Settings and select Spot to run the strategy.
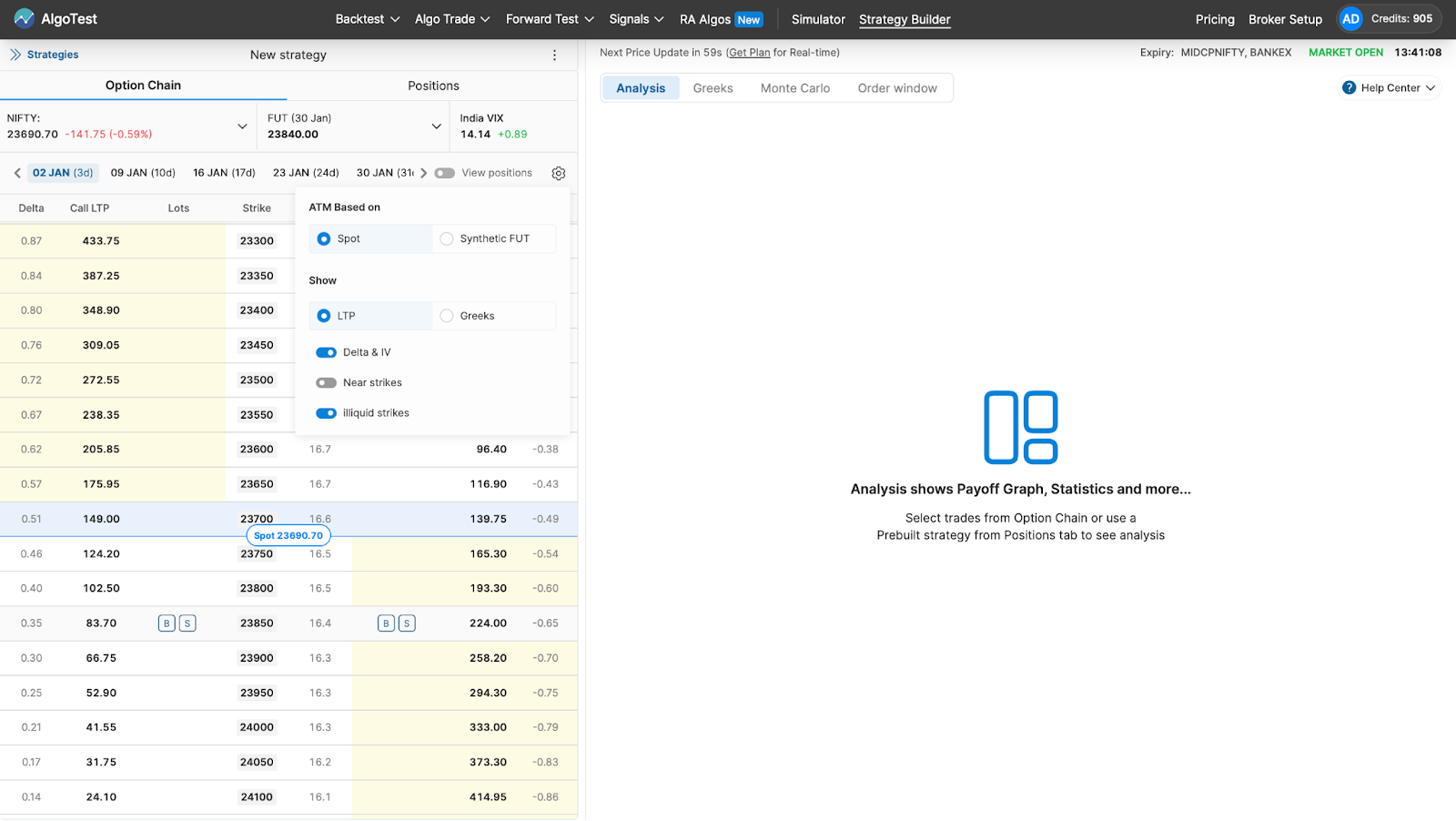
From the Option Chain, we just have to:
- Sell 1 lot of OTM call options
- Sell 1 lot of OTM put options
Click the Buy/Sell button as shown in the image below.
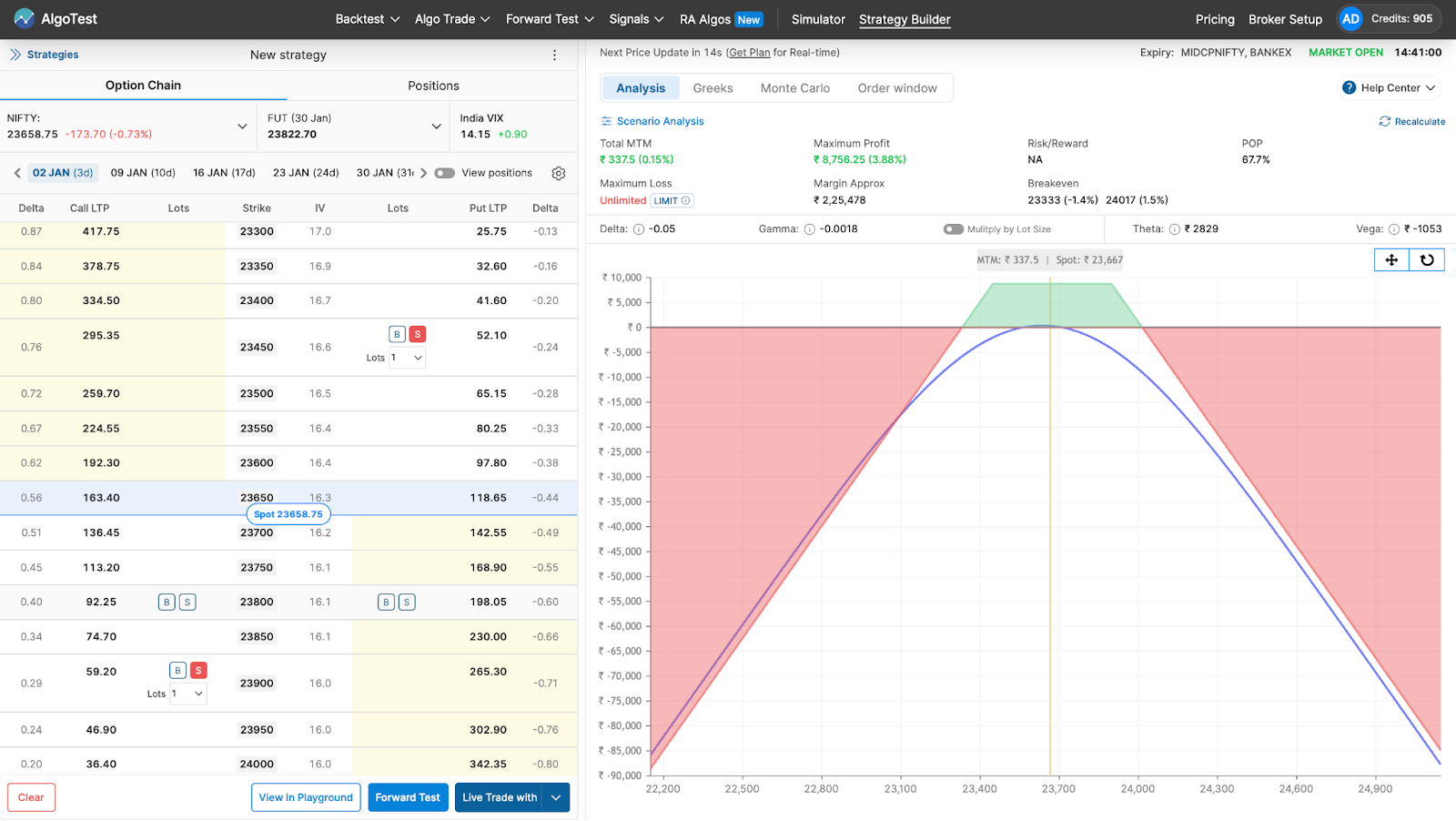
After that, you can deploy it on your broker in one click by clicking the Live Trade With button as shown in the image below. Alternatively, you can forward test (paper trade) it on AlgoTest if you don’t want to deploy it with real money.
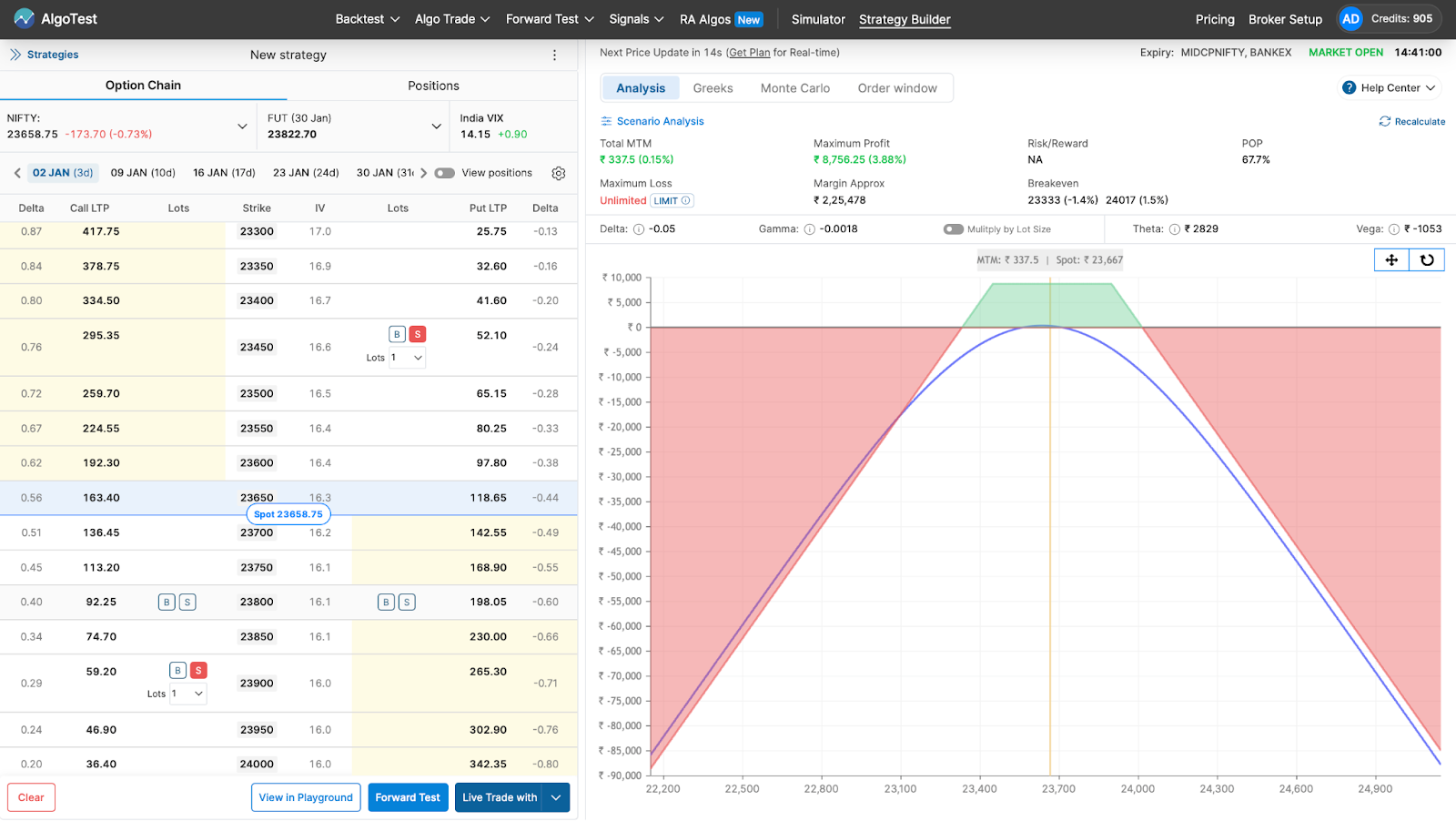
Examples
Long Strangle Example
Suppose a stock is trading at ₹100:
- Buy a ₹110 strike call for ₹2.
- Buy a ₹90 strike put for ₹2.
- Total Cost: ₹4.
Outcomes:
- If the stock price rises above ₹114 or falls below ₹86, you start making a profit.
- If the stock remains between ₹90 and ₹110, your maximum loss is the ₹4 premium paid.
Short Strangle Example
Using the same stock at ₹100:
- Sell a ₹110 strike call for ₹2.
- Sell a ₹90 strike put for ₹2.
- Total Premium Collected: ₹4.
Outcomes:
- If the stock price stays between ₹90 and ₹110, you keep the ₹4 premium as profit.
- If the price moves outside this range, losses can become significant.
When to Use These Strategies
-
Long Strangle:
- Use when expecting significant volatility but unsure of the direction.
- Ideal before events like earnings announcements or major economic news.
-
Short Strangle:
- Apply when expecting stability and minimal price movement.
- Suitable for low-volatility markets or range-bound conditions.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Long Strangle
Advantages:
- Unlimited profit potential if the market moves sharply.
- Risk is limited to the premiums paid.
Disadvantages:
- Losses occur if the market remains stable.
- Can be expensive due to time decay (Theta).
Short Strangle
Advantages:
- Generates income from premiums.
- Effective in stable markets.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of unlimited losses if the market moves sharply.
- Requires significant margin due to potential risks.
Practical Application for AlgoTest Users
AlgoTest simplifies executing and managing both Long and Short Strangle strategies:
- Automation: Automate the setup, execution, and monitoring of these strategies.
- Backtesting: Analyze historical performance to fine-tune strike prices and expirations.
- Volatility Indicators:
- For Long Strangle: Use volatility indicators to time entries effectively.
- For Short Strangle: Monitor market conditions and implied volatility to manage risk.
- Real-Time Monitoring: AlgoTest helps track performance dynamically, allowing for quick adjustments.
Conclusion
The Long and Short Strangle are powerful options strategies for different market conditions:
- Long Strangle: Ideal for betting on volatility.
- Short Strangle: Effective in stable markets.
Using AlgoTest, traders can automate, backtest, and optimize these strategies, ensuring better execution and risk management. By leveraging tools like AlgoTest, traders can enhance their performance and capitalize on market opportunities with confidence.