Bull Put Spread
The Bull Put Spread is a conservative options strategy used when traders have a moderately bullish outlook on an asset. It involves selling a put option at a higher strike price and buying another put option at a lower strike price, both with the same expiration date. The goal is to collect a net credit while limiting potential losses. The premium received from selling the higher strike put is partially offset by the cost of the lower strike put, capping both the profit and the risk.
How It Works
-
Sell a Put Option:
You sell a put option at a higher strike price, collecting a premium. This exposes you to risk if the asset’s price drops below the strike price. -
Buy a Put Option:
Simultaneously, you buy a put option at a lower strike price. This acts as a hedge, limiting your downside risk. -
Net Credit:
The difference between the premium received from selling the higher strike put and the premium paid for the lower strike put is your net credit and maximum profit potential.
Bull Put Spread on AlgoTest
Go to AlgoTest’s Strategy Builder by clicking on this link. You will get an interface as shown in the image below.
Go to Settings and select Spot to run the strategy.
From the Option Chain, we just have to:
- Buy 1 OTM put option
- Sell 1 ITM put option
Click the Buy/Sell button as shown in the image below.
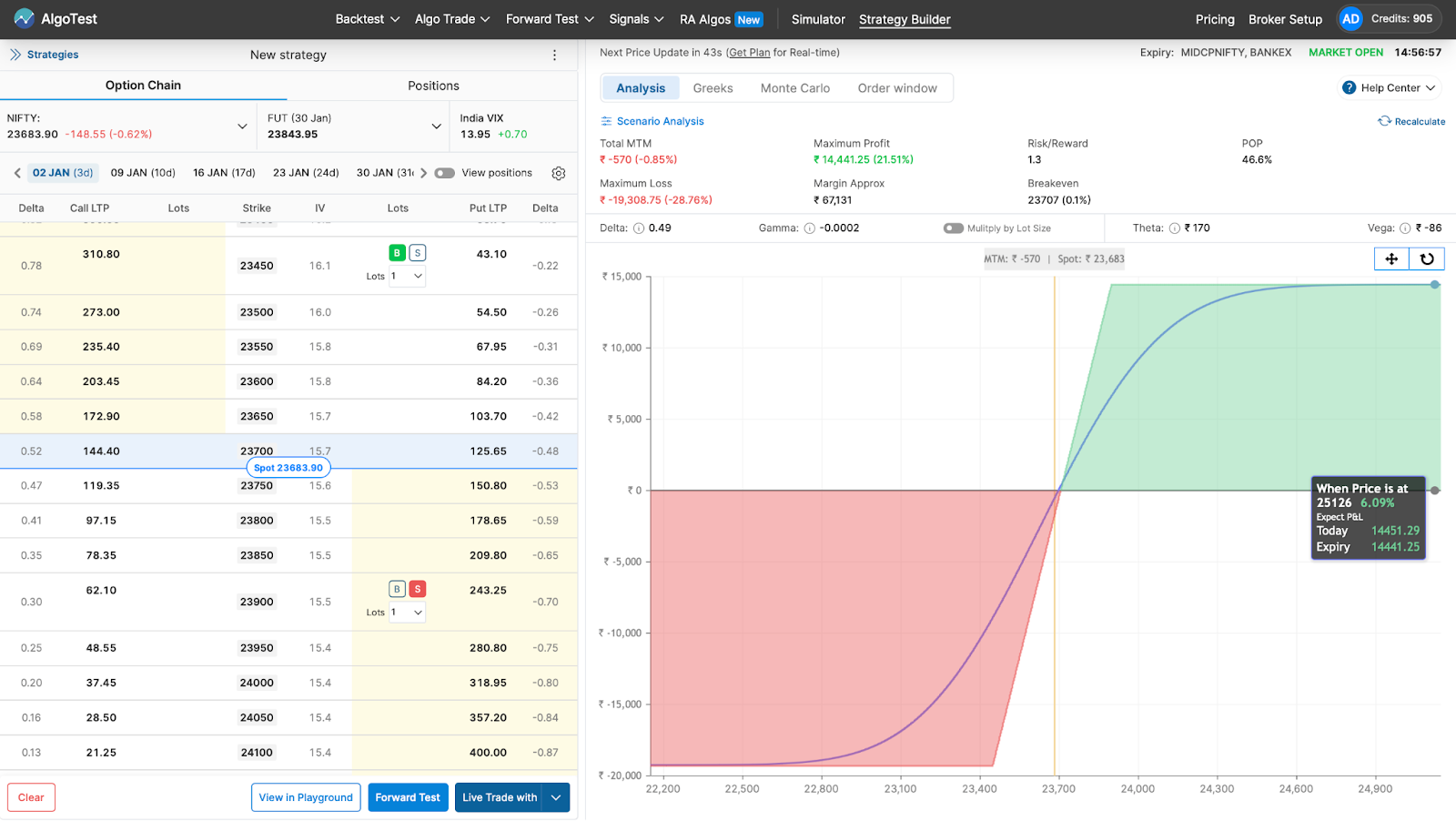
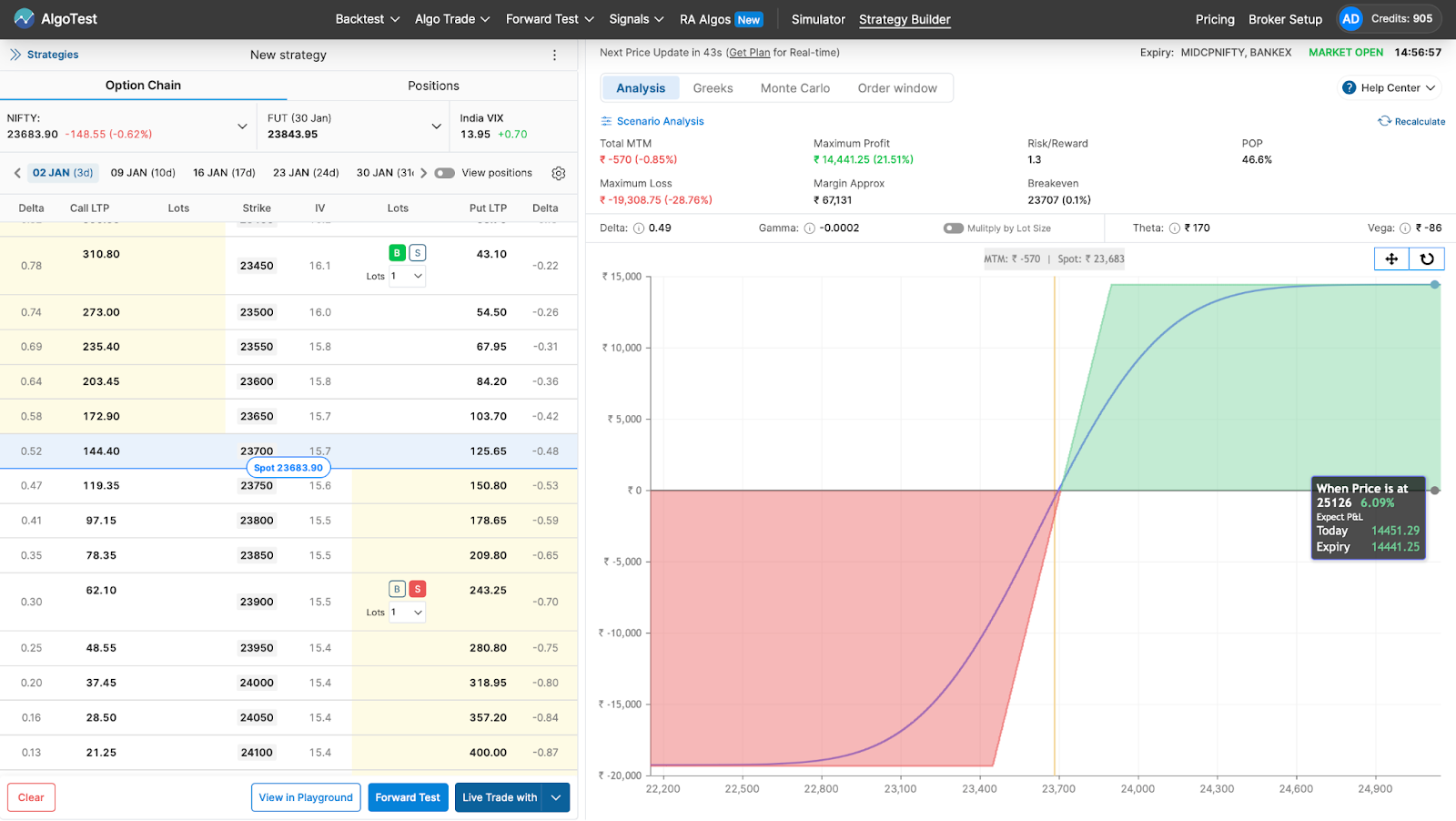
After that, you can deploy it on your broker in one click by clicking the Live Trade With button as shown in the image below. Alternatively, you can forward test (paper trade) it on AlgoTest if you don’t want to deploy it with real money.
Example
Imagine a stock is trading at ₹100. You believe the stock will stay above ₹95 until expiration.
- You sell a put option with a ₹100 strike for ₹5.
- You buy a put option with a ₹95 strike for ₹2.
- The net credit is ₹3, which is your maximum profit.
Outcomes:
-
If the stock stays above ₹100:
- Both options expire worthless, and you keep the ₹3 net credit.
-
If the stock falls below ₹95:
- Your maximum loss is limited to ₹2 (the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit).
When to Use the Bull Put Spread
- Market Outlook: Employ this strategy when you expect the asset’s price to remain stable or increase moderately.
- Risk Management: It’s a great way to generate income with limited risk, especially in markets that are not highly volatile.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- The strategy generates income from the net credit.
- Losses are limited, providing a defined risk profile.
- It requires less margin compared to selling a naked put.
Disadvantages:
- Profit is capped at the net credit, meaning you cannot take full advantage of a significant upward move.
- If the underlying asset drops below the lower strike, you still face a loss, although limited.
Practical Application on AlgoTest
Using AlgoTest, traders can:
- Automate and backtest the Bull Put Spread to assess its performance under various market conditions.
- Automation ensures trades are executed with precision, and backtesting provides insights into how the strategy would have performed historically.
This strategy is perfect for traders looking to earn premium income with a controlled risk profile, making it a reliable choice for those seeking a consistent, lower-risk approach to bullish markets.